Revolutionary technology shortens cardiac scan time, provides high-quality SPECT images
A cardiac SPECT imaging system using self-collimation performs scans 10 to 100 times faster than current SPECT systems, according to new research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2022 Annual Meeting. The advantages of selfcollimation SPECT include dramatically shortened scan time, better image quality, increased patient throughput, and reduced radiation exposure to patients.
“The technology proposed in this work may drive a paradigm shift in all single-photon-emission-based molecular imaging and nuclear medicine technologies,” remarked Tianyu Ma, PhD, associate professor of Engineering Physics at Tsinghua University. “The new detector design opens up a broad range of possibilities for development of new imaging systems with better image quality, higher speed, and better diagnostic accuracy in molecular imaging.”
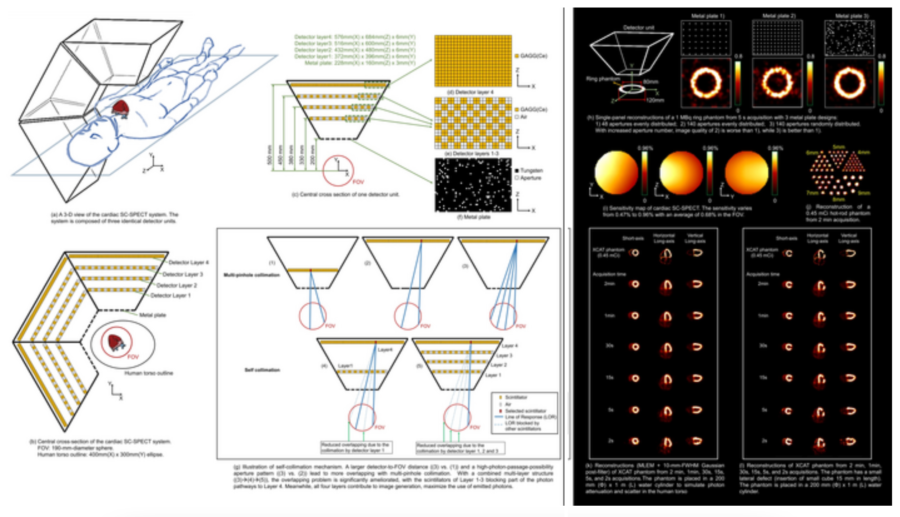
The new system is constructed with the concept of self-collimation; active detectors in a multi-layer architecture carry out the dual functionality of detection and collimation. This concept improves the conventional SPECT paradigm, in which a mechanical collimator is the backbone but also the bottleneck of imaging performance.
“SPECT is an important noninvasive imaging tool for the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with coronary heart disease,” said Debin Zhang, a doctoral student in the Department of Engineering Physics at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China.
“However, conventional SPECT suffers from long scan time and poor image quality as a result of relying on a mechanical collimator. The new SPECT system is capable of performing fast-framed dynamic scans with high quality.”
To break away from the constraints of mechanical collimator, the research team designed a self-collimating cardiac SPECT system. They used a multilayer, interspaced mosaic-patterned detector that carries out a dual function of photon detection and collimation. The signal-to-noise ratio of the system is further improved with a random pattern of apertures on the metal plate, which also functions as part of the collimation. The system had an average sensitivity of 0.68% in the field of view and was able to identify the defect in a cardiac phantom in as little as 2 seconds.
System geometry, imaging mechanism, and performance evaluation of a self-collimating SPECT for fast dynamic cardiac imaging. CREDIT: Debin Zhang, et. al., Tsinghua University, Beijing, China; Zuo-Xiang He, Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, Tsinghua University; and Rutao Yao, University of Buffalo, New York, United States