R-One robotic platform looks set to revolutionise interventional cardiology
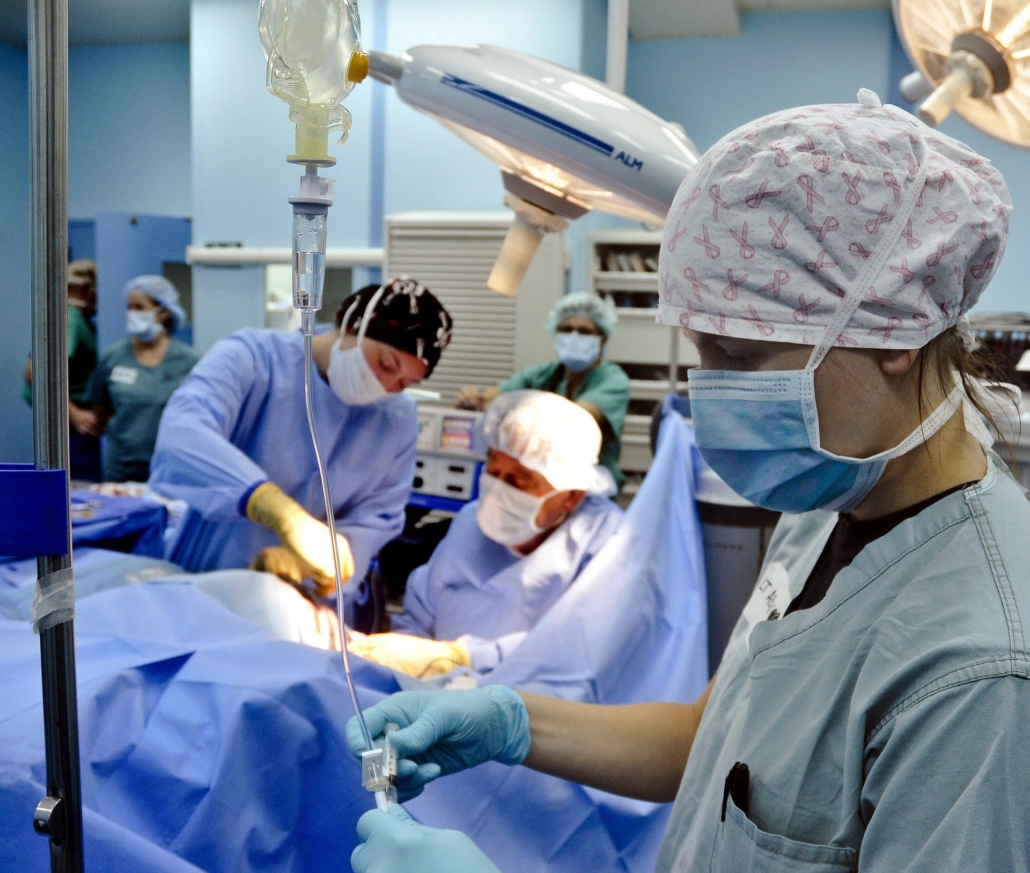
Robocath’s R-One robotic platform has been used to successfully complete the first five robotic coronary angioplasties in Belgium.
Robocath’s R-One robotic platform has been used to successfully complete the first five robotic coronary angioplasties in Belgium.
Neurescue, a Copenhagen, Denmark-based medical device company developing cardiovascular solutions, has received U.S. FDA clearance to market the company’s NEURESCUE device for temporary occlusion of large vessels, including patients requiring emergency control of haemorrhage.
The first-in-human use of Foldax’s biopolymer Tria™ heart valve as a replacement for a diseased mitral valve has shown positive results. The first case was performed by David Heimansohn, MD, at Ascension St. Vincent Hospital, Indianapolis, as part of a U.S. early feasibility research study.
Procyrion, a medical device company developing catheter-deployed pump technology, has successfully treated the first patients in the company’s pilot trial to evaluate the performance of its novel Aortix™ percutaneous mechanical circulatory support (pMCS) device in patients with cardiorenal syndrome (CRS). The company began its pilot trial in Australia and recently expanded to the U.S. after […]
The VAX TRUST consortium was recently established with the aim of addressing vaccine hesitancy in Europe and to help healthcare professionals prepare for meeting with vaccine hesitant individuals. International Hospital speaks to Pia Vuolanto, the head of consortium, about VAX TRUST and the issue of vaccine hesitancy.
Researchers at UC San Francisco have successfully developed a ‘speech neuroprosthesis’ that has enabled a man with severe paralysis to communicate in sentences, translating signals from his brain to the vocal tract directly into words that appear as text on a screen.
The achievement, which was developed in collaboration with the first participant of a clinical research trial, builds on more than a decade of effort by UCSF neurosurgeon Edward Chang, MD, to develop a technology that allows people with paralysis to communicate even if they are unable to speak on their own. The study appears July 15 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“To our knowledge, this is the first successful demonstration of direct decoding of full words from the brain activity of someone who is paralyzed and cannot speak,” said Chang, the Joan and Sanford Weill Chair of Neurological Surgery at UCSF, Jeanne Robertson Distinguished Professor, and senior author on the study. “It shows strong promise to restore communication by tapping into the brain’s natural speech machinery.”
Each year, thousands of people lose the ability to speak due to stroke, accident, or disease. With further development, the approach described in this study could one day enable these people to fully communicate.
Previously, work in the field of communication neuroprosthetics has focused on restoring communication through spelling-based approaches to type out letters one-by-one in text. Chang’s study differs from these efforts in a critical way: his team is translating signals intended to control muscles of the vocal system for speaking words, rather than signals to move the arm or hand to enable typing. Chang said this approach taps into the natural and fluid aspects of speech and promises more rapid and organic communication.
“With speech, we normally communicate information at a very high rate, up to 150 or 200 words per minute,” he said, noting that spelling-based approaches using typing, writing, and controlling a cursor are considerably slower and more laborious. “Going straight to words, as we’re doing here, has great advantages because it’s closer to how we normally speak.”
Over the past decade, Chang’s progress toward this goal was facilitated by patients at the UCSF Epilepsy Center who were undergoing neurosurgery to pinpoint the origins of their seizures using electrode arrays placed on the surface of their brains. These patients, all of whom had normal speech, volunteered to have their brain recordings analyzed for speech-related activity. Early success with these patient volunteers paved the way for the current trial in people with paralysis.
Previously, Chang and colleagues in the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences mapped the cortical activity patterns associated with vocal tract movements that produce each consonant and vowel. To translate those findings into speech recognition of full words, David Moses, PhD, a postdoctoral engineer in the Chang lab and one of the lead authors of the new study, developed new methods for real-time decoding of those patterns and statistical language models to improve accuracy.
But their success in decoding speech in participants who were able to speak didn’t guarantee that the technology would work in a person whose vocal tract is paralyzed. “Our models needed to learn the mapping between complex brain activity patterns and intended speech,” said Moses. “That poses a major challenge when the participant can’t speak.”
In addition, the team didn’t know whether brain signals controlling the vocal tract would still be intact for people who haven’t been able to move their vocal muscles for many years. “The best way to find out whether this could work was to try it,” said Moses.
To investigate the potential of this technology in patients with paralysis, Chang partnered with colleague Karunesh Ganguly, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurology, to launch a study known as “BRAVO” (Brain-Computer Interface Restoration of Arm and Voice). The first participant in the trial is a man in his late 30s who suffered a devastating brainstem stroke more than 15 years ago that severely damaged the connection between his brain and his vocal tract and limbs. Since his injury, he has had extremely limited head, neck, and limb movements, and communicates by using a pointer attached to a baseball cap to poke letters on a screen.
The participant, who asked to be referred to as BRAVO1, worked with the researchers to create a 50-word vocabulary that Chang’s team could recognize from brain activity using advanced computer algorithms. The vocabulary – which includes words such as “water,” “family,” and “good” – was sufficient to create hundreds of sentences expressing concepts applicable to BRAVO1’s daily life.
For the study, Chang surgically implanted a high-density electrode array over BRAVO1’s speech motor cortex. After the participant’s full recovery, his team recorded 22 hours of neural activity in this brain region over 48 sessions and several months. In each session, BRAVO1 attempted to say each of the 50 vocabulary words many times while the electrodes recorded brain signals from his speech cortex.
To translate the patterns of recorded neural activity into specific intended words, the other two lead authors of the study, Sean Metzger, MS and Jessie Liu, BS, both bioengineering doctoral students in the Chang Lab used custom neural network models, which are forms of artificial intelligence. When the participant attempted to speak, these networks distinguished subtle patterns in brain activity to detect speech attempts and identify which words he was trying to say.
To test their approach, the team first presented BRAVO1 with short sentences constructed from the 50 vocabulary words and asked him to try saying them several times. As he made his attempts, the words were decoded from his brain activity, one by one, on a screen.
Then the team switched to prompting him with questions such as “How are you today?” and “Would you like some water?” As before, BRAVO1’s attempted speech appeared on the screen. “I am very good,” and “No, I am not thirsty.”
The team found that the system was able to decode words from brain activity at rate of up to 18 words per minute with up to 93 percent accuracy (75 percent median). Contributing to the success was a language model Moses applied that implemented an “auto-correct” function, similar to what is used by consumer texting and speech recognition software.
Moses characterized the early trial results as a proof of principle. “We were thrilled to see the accurate decoding of a variety of meaningful sentences,” he said. “We’ve shown that it is actually possible to facilitate communication in this way and that it has potential for use in conversational settings.”
Looking forward, Chang and Moses said they will expand the trial to include more participants affected by severe paralysis and communication deficits. The team is currently working to increase the number of words in the available vocabulary, as well as improve the rate of speech.
Both said that while the study focused on a single participant and a limited vocabulary, those limitations don’t diminish the accomplishment. “This is an important technological milestone for a person who cannot communicate naturally,” said Moses, “and it demonstrates the potential for this approach to give a voice to people with severe paralysis and speech loss.”
Co-authors on the paper include Sean L. Metzger, MS; Jessie R. Liu; Gopala K. Anumanchipalli, PhD; Joseph G. Makin, PhD; Pengfei F. Sun, PhD; Josh Chartier, PhD; Maximilian E. Dougherty; Patricia M. Liu, MA; Gary M. Abrams, MD; and Adelyn Tu-Chan, DO, all of UCSF. Funding sources included National Institutes of Health (U01 NS098971-01), philanthropy, and a sponsored research agreement with Facebook Reality Labs (FRL), which completed in early 2021.
Neuroprosthesis for Decoding Speech in a Paralyzed Person with Anarthria. New England Journal of Medicine, 2021; 385 (3): 217 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2027540
By Tracy Hussell
Professor of Inflammatory Disease, University of Manchester
Late last year, I asked: is it safe to have more than one type of COVID-19 vaccine? A trial has now addressed that question, as well as what effect combining different vaccine types has on immunity.
Most COVID-19 vaccines require two doses, and the usual strategy is to give people the same vaccine type for both. But the Com-Cov study, led by the University of Oxford, recruited over 800 participants from across the UK to investigate the effects of giving people different vaccines for their first and second jabs. Two vaccines were studied: those made by Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
So, is mix and match an option? The trial’s results are preliminary, having yet to be reviewed by other scientists, but the answer appears to be yes. Giving people different types of COVID-19 vaccine appears not only to be safe, but also a potential way of boosting protection against the coronavirus.
However, the exact benefits depend on which vaccine goes first and which second. Taking the AstraZeneca vaccine followed by the Pfizer one resulted in a striking increase in antibodies against the coronavirus’s spike protein (a key part of its outer structure) compared to using the AstraZeneca vaccine for both doses or Pfizer followed by AstraZeneca.
Taking the AstraZeneca vaccine followed by Pfizer resulted in a better T cell response than all other combinations of doses. T cells – also known as T lymphocytes – are immune cells that help kill invading germs (such as the coronavirus) and support antibody production.
The Com-Cov study will next look at whether mixing and matching doses like this provides as good results when a larger gap is left between doses. The time between doses in this initial trial was 28 days, but a parallel study is stretching this to 84 days. The results are yet to be reported.
Other researchers have also been studying mixing vaccine types to fight COVID-19. A Spanish study recently reported that people who initially received the AstraZeneca vaccine experienced a massive increase to their antiviral immunity when given a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine – providing more evidence that Pfizer works well as a booster.
To understand why these beneficial effects might be happening, it’s important to understand how the AstraZeneca and Pfizer vaccines work. Both present a key element of the coronavirus – again, the spike protein – to the immune system, but do so using different methods.
The Pfizer approach packs the genetic code for the coronavirus’s spike protein into fatty nanoparticles. When these particles enter the body’s cells, the code is read and copies of the spike protein are produced, leading to an immune response. The AstraZeneca vaccine delivers the same genetic code but uses a weakened form of a common cold virus (an adenovirus) from chimpanzees to carry the code into cells.
When the first vaccine doses are given, it is possible that an immune response is raised not just against the spike protein created, but also against the carriers that are used to deliver the code for it. This is a known issue for treatments or vaccines that use viruses for delivery. If the second dose is then the same, the immunity developed against the carrier will react against the second dose, clearing some of it before robust, protective and long-lasting immunity develops.
This is why Russia’s Sputnik V vaccine – which is based on the same delivery method as the AstraZeneca vaccine – uses two different adenoviruses as carriers for its first and second doses, and has achieved impressive results.
There are additional benefits to mixing vaccine doses on top of improving protection. Logistical problems can arise when a second vaccine dose has to be identical to the first. Producing double the quantity of one vaccine takes time. Boosting with a different vaccine could allow the world’s population to be vaccinated quicker.
Second, if a person reacts badly to their first vaccination, they are more likely to get a second dose if they know it is a different one – and it’s clear that two are needed for good protection. Governments may also decide a certain type of vaccine is less suitable for different groups of people, as has been the case with the AstraZeneca vaccine in younger people in some countries. Having more potential vaccine combinations available may help overcome any public uncertainty in the wake of these sorts of decisions.
Supplying vaccines to some low- and middle-income countries can also be difficult, particularly if they do not have the necessary cold storage requirements for large batches of a vaccine that need to be kept at low temperatures. Including vaccines into the distribution plan that do not need storage at very low temperatures may make widespread vaccine delivery easier.
So there are clearly huge benefits to vaccine mixing. However, this study only looked at two vaccine types – in time, every combination will need to be tested, in every age group and in every ethnicity. Vaccines may also behave differently if mixed in different contexts, for example, against a backdrop of malnutrition or other infectious diseases. These factors will need to be included in future testing too. But for now, this study suggests that a mix-and-match approach to COVID-19 vaccines is an acceptable, useful option.
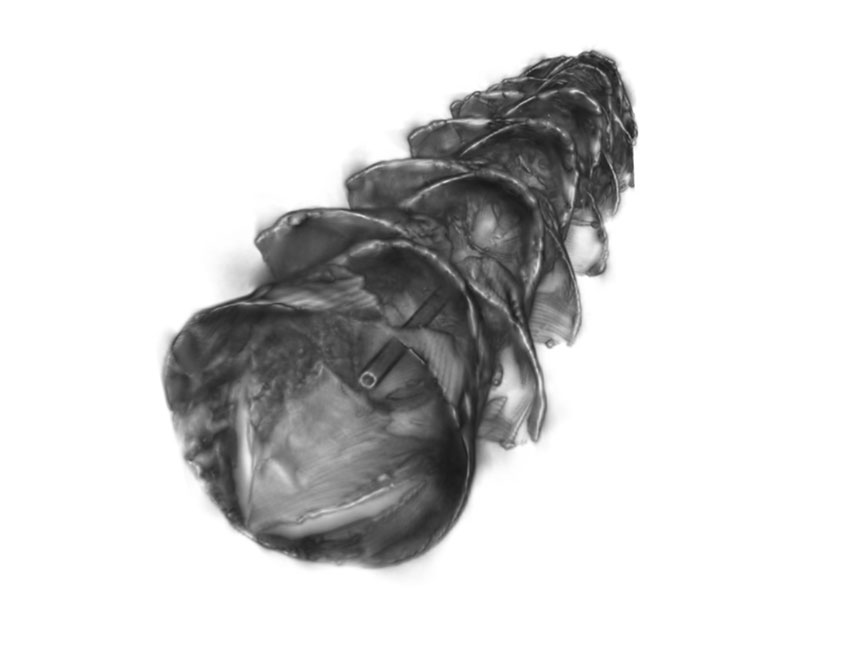

The kirigami-inspired stent
Inspired by kirigami, the Japanese art of folding and cutting paper to create three-dimensional structures, MIT engineers and their collaborators have designed a new type of stent that could be used to deliver drugs to the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, or other tubular organs in the body.
The stents are coated in a smooth layer of plastic etched with small “needles” that pop up when the tube is stretched, allowing the needles to penetrate tissue and deliver a payload of drug-containing microparticles. Those drugs are then released over an extended period of time after the stent is removed.
This kind of localized drug delivery could make it easier to treat inflammatory diseases affecting the GI tract such as inflammatory bowel disease or eosinophilic esophagitis, says Giovanni Traverso, an MIT assistant professor of mechanical engineering, a gastroenterologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and the senior author of the study.
“This technology could be applied in essentially any tubular organ,” Traverso says. “Having the ability to deliver drugs locally, on an infrequent basis, really maximizes the likelihood of helping to resolve patients’ conditions and could be transformative in how we think about patient care by enabling local, prolonged drug delivery following a single treatment.”
Sahab Babaee, an MIT research scientist, is the lead author of the paper, which appears in Nature Materials.
Inflammatory diseases of the GI tract, such as IBD, are often treated with drugs that dampen the body’s immune response. These drugs are usually injected, so they can have side effects elsewhere in the body. Traverso and his colleagues wanted to come up with a way to deliver such drugs directly to the affected tissues, reducing the likelihood of side effects.
Stents could offer a way to deliver drugs to a targeted portion of the digestive tract, but inserting any kind of stent into the GI tract can be tricky because digested food is continuously moving through the tract. To make this possibility more feasible, the MIT team came up with the idea of creating a stent that would be inserted temporarily, lodge firmly into the tissue to deliver its payload, and then be easily removed.
The stent they designed has two key elements – a soft, stretchy tube made of silicone-based rubber, and a plastic coating etched with needles that pop up when the tube is stretched.
“The novelty of our approach is that we used tools and concepts from mechanics, combined with bioinspiration from scaly-skinned animals, to develop a new class of drug-releasing systems with the capacity to deposit drug depots directly into luminal walls of tubular organs for extended release,” Babaee says. “The kirigami stents were engineered to provide a reversible shape transformation: from flat, to 3D, buckled-out needles for tissue engagement, and then to the original flat shape for easy and safe removal.”
In this study, the MIT team coated the plastic needles with microparticles that can carry drugs. After the stent is inserted endoscopically, the endoscope is used to inflate a balloon inside the tube, causing the tube to elongate. As the tube stretches, the pulling motion causes the needles in the plastic to pop up and release their cargo.
“It’s a dynamic system where you have a flat surface, and you can create these little needles that pop up and drive into the tissue to do the drug delivery,” Traverso says.
For this study, the researchers created kirigami needles of several different sizes and shapes. By varying those features, as well as the thickness of the plastic sheet, the researchers can control how deeply the needles penetrate into the tissue. “The advantage of our system is that it can be applied to various length scales to be matched with the size of the target tubular compartments of the gastrointestinal tract or any tubular organs,” Babaee says.
The researchers tested the stents by endoscopically inserting them into the oesophagus of pigs. Once the stent was in place, the researchers inflated the balloon inside the stent, allowing the needles to pop up. The needles, which penetrated about half a millimetre into the tissue, were coated with microparticles containing a drug called budesonide, a steroid that is used to treat IBD and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Once the drug-containing particles were deposited in the tissue, the researchers deflated the balloon, flattening out the needles so the stent could be endoscopically removed. This process took only a couple of minutes, and the microparticles then stayed in the tissue and gradually released budesonide for about one week.
Depending on the composition of the particles, they could be tuned to release drugs over an even longer period of time, Traverso says. This could make it easier to keep patients on the correct drug schedule, because they would no longer need to take the drug themselves, but would periodically receive their medicine via temporary insertion of the stent. It would also avoid the side effects that can occur with systemic drug administration.
The researchers also showed that they could deliver the stents into blood vessels and the respiratory tract. They are now working on delivering other types of drugs and on scaling up the manufacturing process, with the goal of eventually testing the stents in patients.
The WHO Council on the Economics of Health for All, which comprises leading economists and health experts from across the globe, has called on governments, the scientific and medical community and private sector leaders to re-design the health innovation ecosystem toward delivering health technologies for the common good.
In the Council’s first brief, its members called on the public and private sectors to work collaboratively to deliver needed vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics, and other essential health supplies that are available equitably to those who can benefit.
The Council Brief recommends both immediate and long-term action, urging all stakeholders to work towards creating a health innovation ecosystem characterized by purpose-driven and symbiotic public-private partnerships that put the common good front and centre.
“Mobilizing money to throw at solutions that fail to address the underlying causes of longstanding structural problems will not be sufficient,” according to the Council Brief. “We all must look forward towards re-imagining health innovation as part of a new economic ecosystem that can deliver Health for All.”
The Council has made clear that just patching up the existing system will not work. Deep change is needed on how intellectual property rights are governed to drive collective intelligence, how corporate governance is structured, and how the benefits of public investments are shared to avoid the current dynamic of sharing risks but privatizing rewards.
To build an inclusive end-to-end health innovation ecosystem able to deliver the appropriate medical technologies required to achieve Health for All equitably, the following building blocks are critical:
In the short-term, the Council, in its brief, adds its voice to the growing calls for urgent action in four areas:
The Council’s brief came ahead of the G7 Leaders’ Summit under the U.K.’s Presidency, which aims to build back better from the COVID-19 pandemic, including by strengthening resilience against future pandemics; and following the Seventy-fourth World Health Assembly and the G20 Global Health Summit co-hosted by Italy and the EU earlier this month.
The Council, which was established by the World Health Organization in November 2020, is chaired by noted economist Professor Mariana Mazzucato, Professor of the Economics of Innovation and Public Value and Founding Director in the Institute for Innovation and Public Purpose at University College London.
Its patron is H.E. Sanna Marin, Prime Minister of Finland.
As vaccine nationalism and inequitable distribution continue to plague the global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, epidemiologists from leading academic institutes around world have issued a stark warning that so-called ‘variants of concern’ to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, could render current vaccines ineffective in less than a year. Callan Emery reports.
April 2024
The medical devices information portal connecting healthcare professionals to global vendors
Prins Hendrikstraat 1
5611HH Eindhoven
The Netherlands
info@interhospi.com
PanGlobal Media IS not responsible for any error or omission that might occur in the electronic display of product or company data.
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
Accept settingsHide notification onlyCookie settingsWe may ask you to place cookies on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience and to customise your relationship with our website.
Click on the different sections for more information. You can also change some of your preferences. Please note that blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience on our websites and the services we can provide.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to provide the website, refusing them will affect the functioning of our site. You can always block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and block all cookies on this website forcibly. But this will always ask you to accept/refuse cookies when you visit our site again.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies, but to avoid asking you each time again to kindly allow us to store a cookie for that purpose. You are always free to unsubscribe or other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies, we will delete all cookies set in our domain.
We provide you with a list of cookies stored on your computer in our domain, so that you can check what we have stored. For security reasons, we cannot display or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser's security settings.
.These cookies collect information that is used in aggregate form to help us understand how our website is used or how effective our marketing campaigns are, or to help us customise our website and application for you to improve your experience.
If you do not want us to track your visit to our site, you can disable this in your browser here:
.
We also use various external services such as Google Webfonts, Google Maps and external video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data such as your IP address, you can block them here. Please note that this may significantly reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will only be effective once you reload the page
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Maps Settings:
Google reCaptcha settings:
Vimeo and Youtube videos embedding:
.U kunt meer lezen over onze cookies en privacy-instellingen op onze Privacybeleid-pagina.
Privacy policy