New Cell Atlas of COVID lungs reveals why SARS-CoV-2 is different and deadly
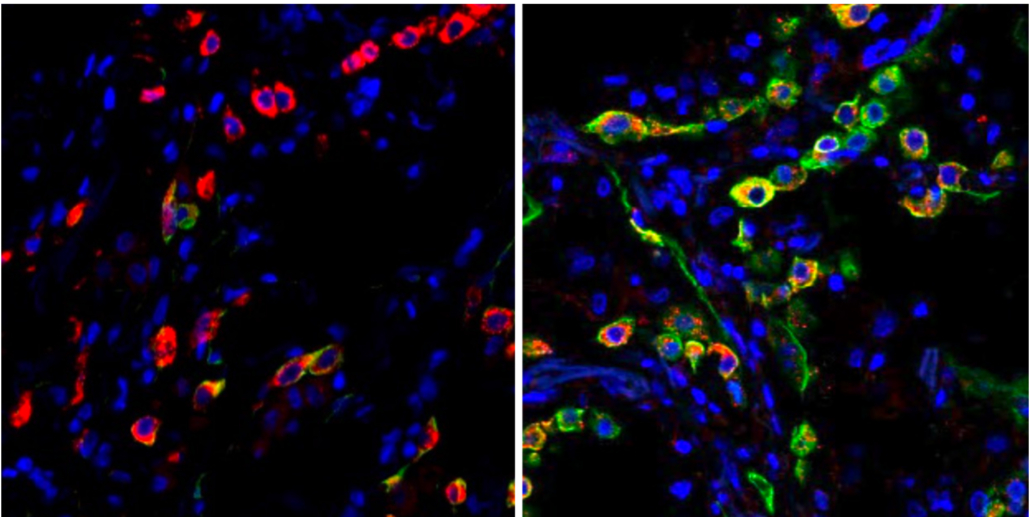
Lung cells in patients with severe COVID become trapped in a state (indicated by the green color) that prevents the cells from repairing damage caused by the infection. The left image shows cells from a healthy lung; the right image shows lung cells from a patient who died from COVID-19. Images: Benjamin Izar / Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
A new study published in Nature [1] draws the most detailed picture yet of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lung, revealing mechanisms that result in lethal COVID-19, and may explain long-term complications and show how COVID-19 differs from other infectious diseases.
Led by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, the study found that in patients who died of the infection, COVID-19 unleashed a detrimental trifecta of runaway inflammation, direct destruction and impaired regeneration of lung cells involved in gas exchange, and accelerated lung scarring.
Though the study looked at lungs from patients who had died of the disease, it provides solid leads as to why survivors of severe COVID may experience long-term respiratory complications due to lung scarring.
“It’s a devastating disease, but the picture we’re getting of the COVID-19 lung is the first step towards identifying potential targets and therapies that disrupt some of the disease’s vicious circuits. In particular, targeting cells responsible for pulmonary fibrosis early on could possibly prevent or ameliorate long-term complications in survivors of severe COVID-19,” says Benjamin Izar, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine, who led a group of more than 40 investigators to complete in several months a series of analyses that usually takes years.
This study and a companion paper [2] led by researchers at Harvard/MIT, to which the Columbia investigators also contributed, were published in the journal Nature on April 29.
Study creates atlas of cells in COVID lung
The new study is unique from other investigations in that it directly examines lung tissue (rather than sputum or bronchial washes) using single-cell molecular profiling that can identify each cell in a tissue sample and record each cell’s activity, resulting in an atlas of cells in COVID lung.
“A normal lung will have many of the same cells we find in COVID, but in different proportions and different activation states,” Izar says. “In order to understand how COVID-19 is different compared to both control lungs and other forms of infectious pneumonias, we needed to look at thousands of cells, one by one.”
Izar’s team examined the lungs of 19 individuals who died of COVID-19 and underwent rapid autopsy (within hours of death) – during which lung and other tissues were collected and immediately frozen – and the lungs of non-COVID-19 patients. In collaboration with investigators at Cornell University, the researchers also compared their findings to lungs of patients with other respiratory illnesses.
Drugs targeting IL-1ß may reduce inflammation
Compared to normal lungs, lungs from the COVID patients were filled with immune cells called macrophages, the study found.
Typically during an infection, these cells chew up pathogens but also regulate the intensity of inflammation, which also helps in the fight.
“In COVID-19, we see expansion and uncontrolled activation of macrophages, including alveolar macrophages and monocyte-derived macrophages,” Izar says. “They are completely out of balance and allow inflammation to ramp up unchecked. This results in a vicious cycle where more immune cells come in causing even more inflammation, which ultimately damages the lung tissue.”
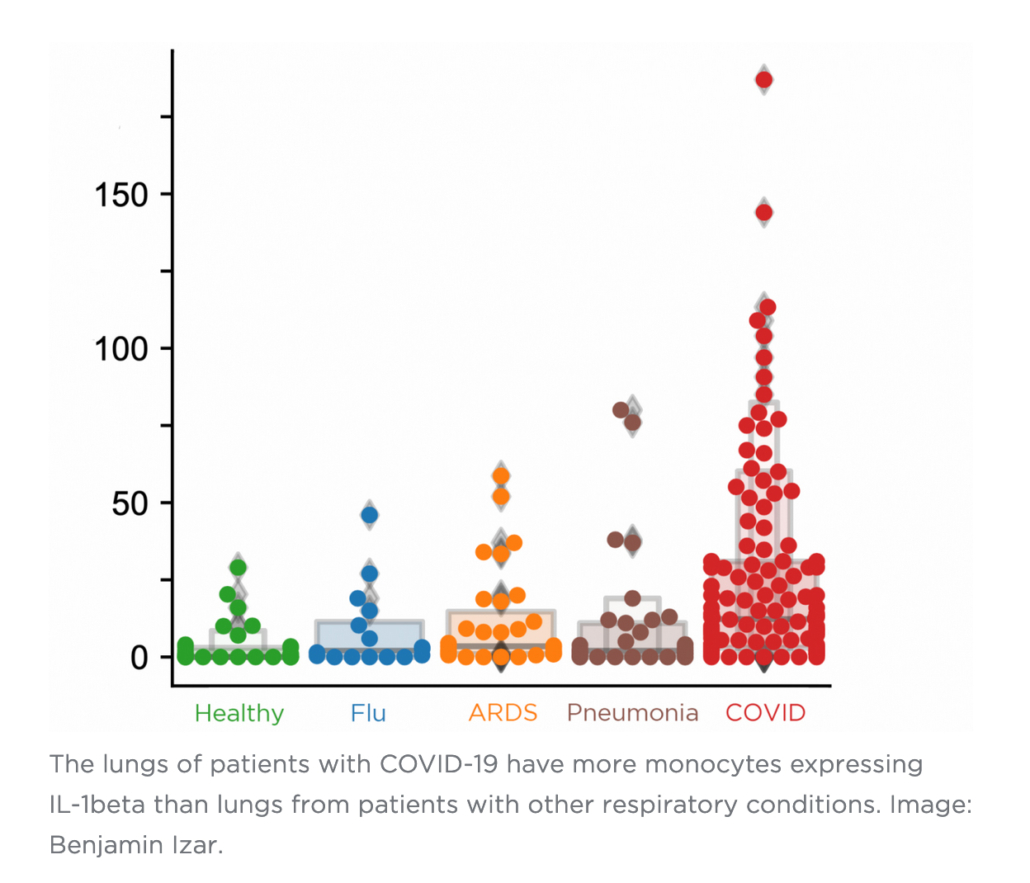
One inflammatory cytokine in particular, IL-1ß, is produced at a high rate by these macrophages.
“Unlike other cytokines such as IL-6, which appears to be universally prevalent in various pneumonias, IL-1ß production in macrophages is more pronounced in COVID-19 compared to other viral or bacterial lung infections,” Izar says. “That’s important because drugs exist that tamp down the effects of IL-1ß.”
Some of these drugs are already being tested in clinical trials of COVID patients.
Severe COVID also prevents lung repair
In a typical infection, a virus damages lung cells, the immune system clears the pathogen and the debris, and the lung regenerates.
But in COVID, the new study found that not only does SARS-CoV-2 virus destroy alveolar epithelial cells important for gas exchange, the ensuing inflammation also impairs the ability of the remaining cells to regenerate the damaged lung.
Though the lung still contains cells that can do the repairs, inflammation permanently traps these cells in an intermediate cell state and leaves them unable to complete the last steps of differentiation needed for replacement of mature lung epithelium.
“Among others, IL-1ß appears to be a culprit in inducing and maintaining this intermediate cell state,” says Izar, “thereby linking inflammation and impaired lung regeneration in COVID-19. This suggests that in addition to reducing inflammation, targeting IL-1ß may help take the brakes off cells required for lung repair.”
Preventing accelerated fibrosis
The researchers also found a large number of specific fibroblast cells, called pathological fibroblasts, that create rapid scarring in COVID-19 lungs. When the fibroblast cells fill the lung with scar tissue, a process called fibrosis, the lung has less space for cells involved in gas exchange and is permanently damaged.
Given the importance of pathological fibroblasts in the disease, Izar’s team closely analysed the cells to uncover potential drug targets. An algorithm called VIPER, developed previously by Andrea Califano, Dr, chair of systems biology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, identified several molecules in the cells that play an important role and could be targeted by existing drugs.
“This analysis predicted that inhibition of STAT signalling could alleviate some of the deleterious effects caused by pathological fibroblasts,” Izar says.
“Our hope is that by sharing this analysis and massive data resource, other researchers and drug companies can begin to test and expand on these ideas and find treatments to not only treat critically ill patients, but also reduce complications in people who survive severe COVID-19.”
References
[1] A molecular single-cell lung atlas of lethal COVID-19. Nature (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03569-1
[2] COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03570-8



 In May 2020, a team led by thoracic surgeon Konrad Hoetzenecker of the Department of Surgery of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital performed a lung transplant on a 44-year-old patient who had been seriously ill with Covid-19, making her the first patient in Europe to receive a lung transplant for this indication. The Vienna lung transplantation programme now plays a leading role in an international consortium comprising experts from the USA, Europe and Asia. Based on the expertise from Vienna, approximately 40 transplants have now been carried out on Covid-19 patients throughout the world.
In May 2020, a team led by thoracic surgeon Konrad Hoetzenecker of the Department of Surgery of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital performed a lung transplant on a 44-year-old patient who had been seriously ill with Covid-19, making her the first patient in Europe to receive a lung transplant for this indication. The Vienna lung transplantation programme now plays a leading role in an international consortium comprising experts from the USA, Europe and Asia. Based on the expertise from Vienna, approximately 40 transplants have now been carried out on Covid-19 patients throughout the world.