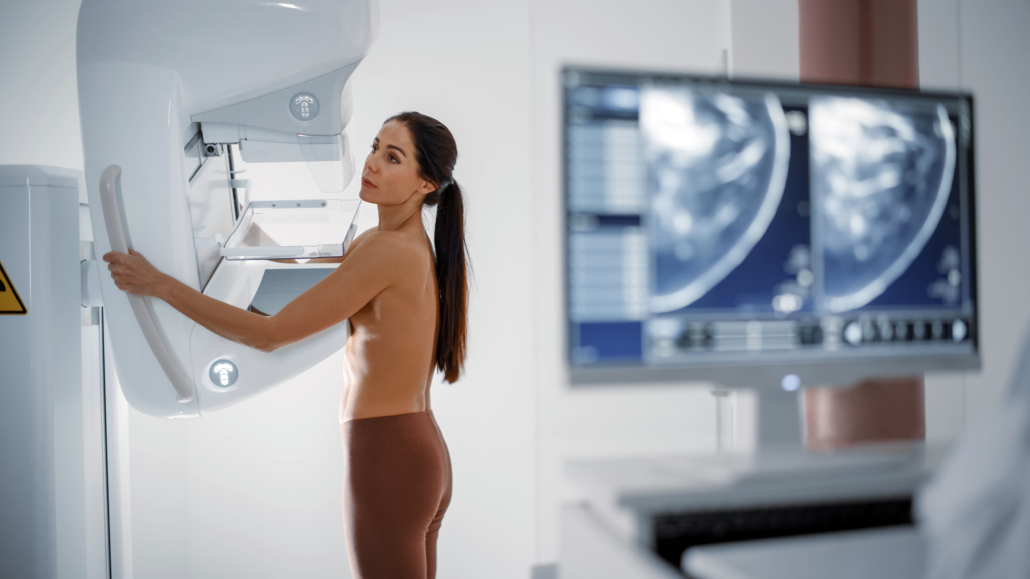
Bio-Gate partnership Hologic and Bayer set up international partnership to provide contrast-enhanced mammography package
Hologic and Bayer has established an international partnership to deliver contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) solutions to improve the detection of breast cancer for women in multiple countries across the European, Canadian and Asia Pacific regions.
CEM is a highly sensitive and relatively low-cost breast imaging modality that combines digital mammography with the administration of a contrast agent to support breast cancer diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
The partnership brings together the companies’ leading technologies (Hologic mammography gantries and Bayer CEM-approved injection systems) to enable the administration of contrast media during a mammography examination. With the new agreement, Bayer and Hologic aim to support radiologists and their teams’ needs by providing a comprehensive product package along with the hands-on training needed to effectively implement CEM into their facility’s workflow.
“Over the past several years, we’ve seen an increased interest in contrast-enhanced mammography as an additional diagnostic modality. Our partnership with Bayer will enable clinicians around the world to offer CEM as part of the breast cancer diagnostic workflow,” said Tanja Brycker, Vice President, Strategic Development, Breast and Skeletal Health and GYN Solutions at Hologic.
Gerd Krueger, President of Radiology at Bayer, commented: “We are excited to join forces with Hologic to deliver a comprehensive solution to our customers and increase access to an emerging breast imaging modality that can help improve diagnostic accuracy as well as provide an alternative imaging option for many women who need it.”
In 2020, there were 2.3 million women diagnosed with breast cancer and 685,000 deaths globally, according to the World Health Organization. Breast cancer treatment can be very effective, especially when the disease is identified early.
The value of CEM as an adjunct to mammography is affirmed by an increasing number of independent scientific publications. It can be performed as part of an everyday clinical practice and used in various clinical settings, such as inconclusive findings in previous imaging procedures, or pre-operative assessment of the extent of the disease. It can also be a helpful tool when MRI is unavailable or contraindicated.