3D navigation system enhances minimally invasive treatment of vascular disease
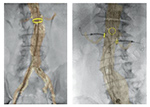
The VesselNavigator is a 3D catheter navigation system to guide the minimally invasive treatment of patients with vascular diseases such as aortic aneurysms. It is designed for use in conjunction with Philips’interventional X-ray systems, enhances the precision and accuracy of stent placement, while at the same time significantly reducing contrast medium usage. As a result, minimally invasive treatment options will be available to patients previously unable to benefit from new image-guided intervention techniques. Developed in collaboration with clinical partners such as the University Hospital Cologne (Germany) and the University Hospital Ghent (Belgium), VesselNavigator complements Philips’current imageguided therapy portfolio within the field of endovascular and hybrid suite solutions. It addresses the need for advanced 3D live-image guidance solutions, as the treatment for vascular disease is experiencing a major transition from open surgery to minimally invasive procedures, with such procedure volumes growing at high single-digit rates. During endovascular procedures a catheter is manoeuvred, with the aid of image guidance, through major arteries or veins in order to locally position and deploy implants such as stents to reinforce the wall of the affected blood vessel. Using conventional 2D X-ray image guidance, clinicians oft en perceive the visualization of the vessel anatomy during these procedures as if a dimension is missing, adding to procedure complexity. Many are more familiar with open surgery, during which they can physically see and touch the blood vessels they are trying to repair. VesselNavigator brings back the 3D anatomy they were used to seeing in open surgery. It can be used for all types of endovascular procedures, but one of its key applications is guidance during the treatment of aortic aneurysms, which if left untreated could lead to severe complications such as massive internal bleeding. At the location of the aneurysm, the aorta oft en has smaller side branches, such as those that supply blood to the patient’s kidneys. Custom-made stents are therefore oft en made with dedicated openings that need to be precisely registered with these feeding vessels in order to repair the aorta and maintain critical blood flow to other abdominal organs. With conventional X-ray imaging it is very challenging to position the stent in the precise orientation. Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair is therefore a very complex procedure, and the more time it takes, the more contrast medium is needed for X-ray visualization and guidance in order to succeed. Vessel- Navigator fuses live interventional X-ray images with pre-acquired 3D MRI or CT images of the patient’s vascular structures. The resulting 3D colour-coded images of the vessels provide enhanced real-time visual guidance, making it easier to manoeuvre through the vascular network without the need to enhance the X-ray visualization with the repeated use of an injected contrast medium. In recent studies, VesselNavigator has been shown to reduce contrast medium usage by 70% and procedure times by 18%, contributing to more patient friendly, more efficient and more cost effective treatment of vascular conditions. With a growing population of elderly and diabetic people who suffer from poor kidney function, reducing contrast medium requirements will open up endovascular treatments to a wider range of patients. The strong growth in image-guided therapy procedures is driven by the significant benefits they off er for healthcare systems and patients, including reduced patient trauma, shorter hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs.